Does modularity mean the
Extinction
of the assembly line?
Extinction
of the assembly line?
The traditional assembly line is quickly becoming smarter, manufacturing had primarily been characterized by craftsmanship and uniqueness, when consumers used to buy customized items that had been created just for them, and which often became points of pride for the makers.
However, Henry Ford would soon come along and change all of that, and manufacturing would instead become defined by economies of scale, repeatability and affordability.
Now almost 100 years later, Industry 4.0 has begun ushering in an era of customization-with the key difference being that, this time, it is happening on an unprecedented scale. Technologies like IIoT, big data, 3D printing, and robotics are all at the core of this new revolution. Traditionally, personalization meant losing some volume, and was only available only at a premium. However, consumers can now place orders for customized cars, mobile phones, and even machines, which will be all manufactured at scale and then delivered to each consumer on-time. This is made possible due to the ability of robots and other machines to be rapidly configured and then reconfigured to adapt to all the different specifications that the customer provides.
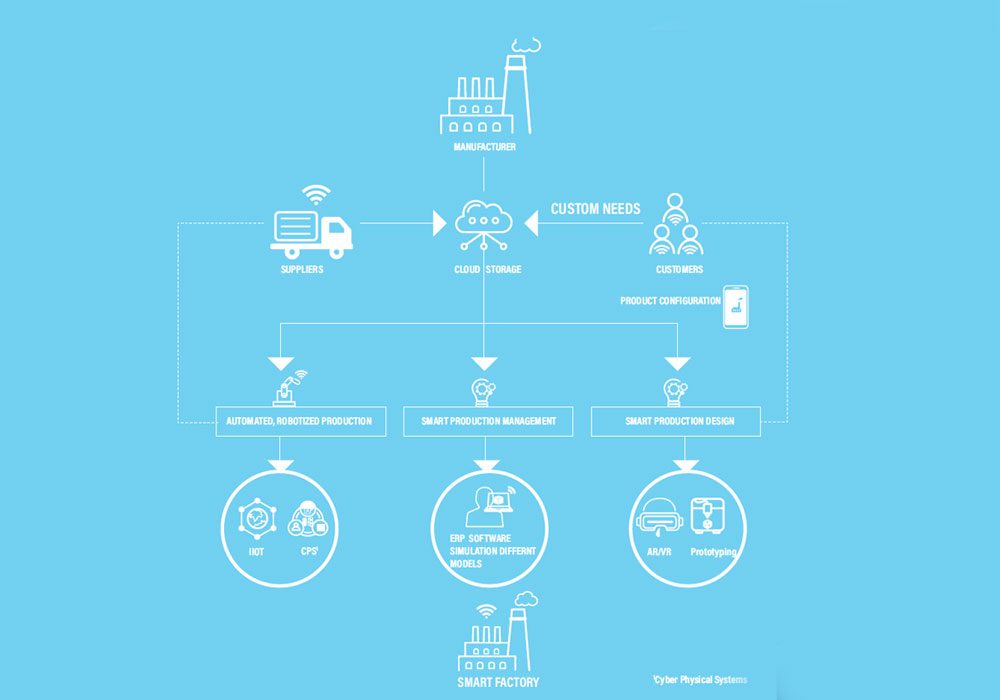
Interestingly, these trends are not only evident within the B2C segment, but also in B2B. For example, Hoffman, a subsidiary of Pentair, provides custom electrical closets and website Flying-parts.com, which manufactures co-designed parts at a fraction of the cost of those being offered by traditional aviation parts manufacturers. Some other, more conventional B2B sectors (such as construction and glass manufacturing) are also beginning to adopt mass customization models, with a keen focus on 3D printing technologies.
Lean customization, is another interesting trend arising from mass customization in which manufacturers make use of just-in-time inventory and digital technologies to produce items at scale, and at low prices.
A good example of this is Liberty Bottleworks, whose plant in Portland, Oregon manufactures about 70,000 aluminum drinking bottles every month. Even though the company’s size and scale doesn’t come close to that of Chinese manufacturers, its bottles are still effectively competing with them in retail stores all throughout the US. According to the company’s COO, Ryan Clark, the main reason for this is lean customization, which allows for consumers to choose the exact shape, size, color and graphic that they want on their bottle, at no extra cost to the company.
Over the last two decades, major corporations have been outsourcing their manufacturing to low cost regions such as Greater China (electronics), Mexico (clothing), Vietnam (shoes), and so on. And although these global supply chains come with the attractive benefit of cheap labour (resulting in low product costs), disadvantages such as long lead-times, low flexibility, instability in supply chains, poor quality standards and rising labour costs have all begun to drive manufacturing to be geographically closer to the consumer.
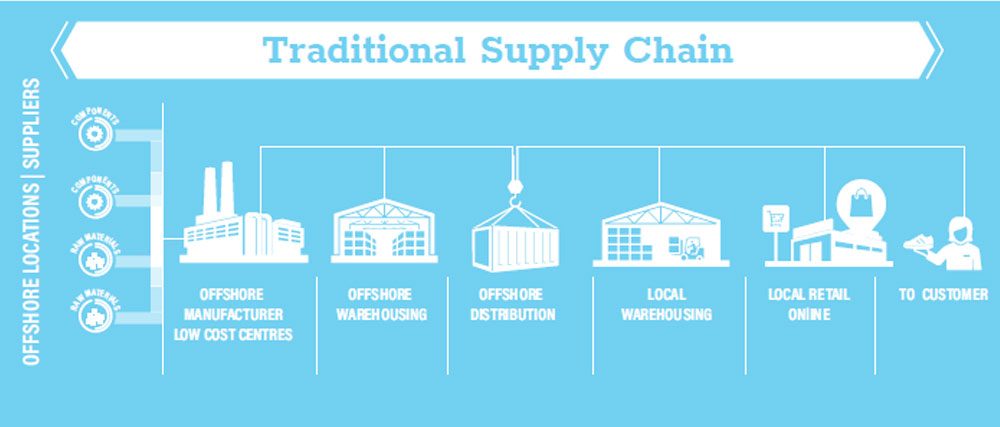
The largest catalyst of this change, however, is the advent of the smart factory-which, when coupled with the increasing consumer appetite to have customized products delivered to them quickly, is starting to push production back closer to the markets from which the demand originates. One of the major benefits to this approach is the shortening of the supply chain; distant mass production centers simply have too many stages in the value chain, including transportation, warehousing, insurance, manpower, etc., which not only serves to increase costs manifold, but also extends the time it takes to get a new product to market. For example, it took Adidas 18 months to get a new shoe to market from the design phase from its factory in Vietnam. This is a very long time, especially in a market like trainers, which is particularly sensitive to shifting trends. Realizing this, the company opened its first automated Speedfactory in Germany in 2015, soon followed by another one in Atlanta, Georgia in April 2018, with Adidas estimating for the two factories to have produced one million pairs of shoes by 2020.
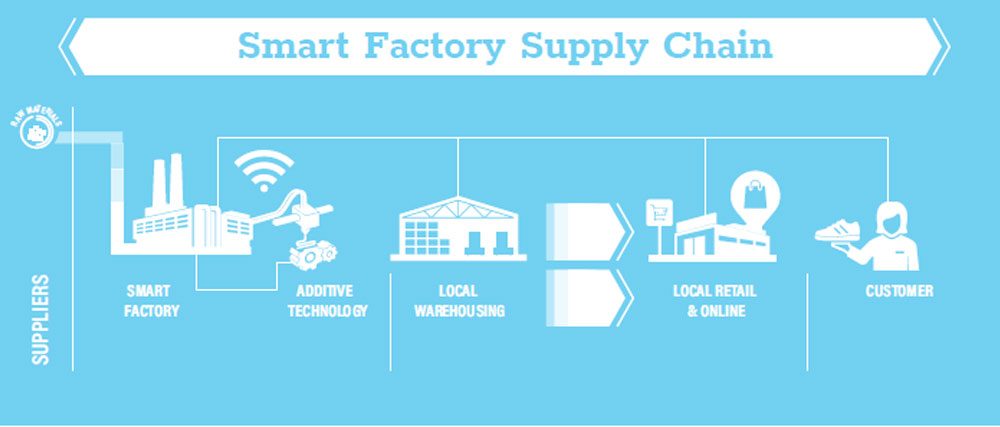
According to Herbert Hainer, former CEO of Adidas, smart manufacturing is taking the industry towards an on-demand manufacturing model which will see customized shoes being delivered within as quickly as a day of their creation. Apart from a drastic reduction in time, this trend will also be crucial in keeping up with the growing demand for customization.
“In a sense we will re-shore production more and more. The future is in more
mass customisation and this means more local production – because we have to shorten
the logistics chain from the production side to the side of the user.”
-Dr Detlef Zühlke. Chairman at the SmartFactoryKL Technology- Initiative
1: Backshoring (also known as onshoring or inshoring) is the process
of moving the production from low cost countries back to the
home countries, despite higher labour costs.
Source: German Manufacturing Survey 2015, Fraunhofer ISI
It’s been about 100 years since Henry Ford gave the automotive industry its first assembly line. Since then, cars have been manufactured in a fixed, sequenced line consisting of pre-defined, rigid processes. In other words, once an assembly line is designed for a particular model, it cannot be changed throughout the lifecycle of a car, and dictates the intra-logistical processes of the production and supply chain.Because of these restrictions, if an auto manufacturer wants to release a modified version of a particular model, it cannot do so without first creating a different assembly line and thereby incurring huge costs. Other industries (such as apparel, pharmaceutical and chemical) are also facing a similar problem in the face of the increasing demand for customization. To create an agile and flexible production process, companies are now making use of the concept of modularization.








Subscribe and get industry facts, success stories, expert advice and industry reports on all things industry 4.0
We promise not to pester you with daily news or weekly bulletins that end up in your junk mail.
